
For a long, long time physicists treated this interaction as a cosmic impossibility — a mathematical dead end so absolute it was taught almost with the certainty of Newton's laws and the elegance of Einstein's equations. Zero, in quantum physics, isn't a shrug; it's a verdict. And this particular verdict had stood unchallenged for decades.
But every so often, science gets a jolt — a falling apple, a bending beam of starlight… or, in 2026, an AI model that refuses to accept “impossible” as an answer.
A new research paper co-authored by leading theoretical physicists and OpenAI researchers has revealed that this interaction, involving particles called gluons, can in fact, occur under very specific conditions. What's more, the key formula describing this interaction was first identified with the help from GPT 5.2, which simplified the complex equations and spotted a pattern that physicists hadn't fully recognised.
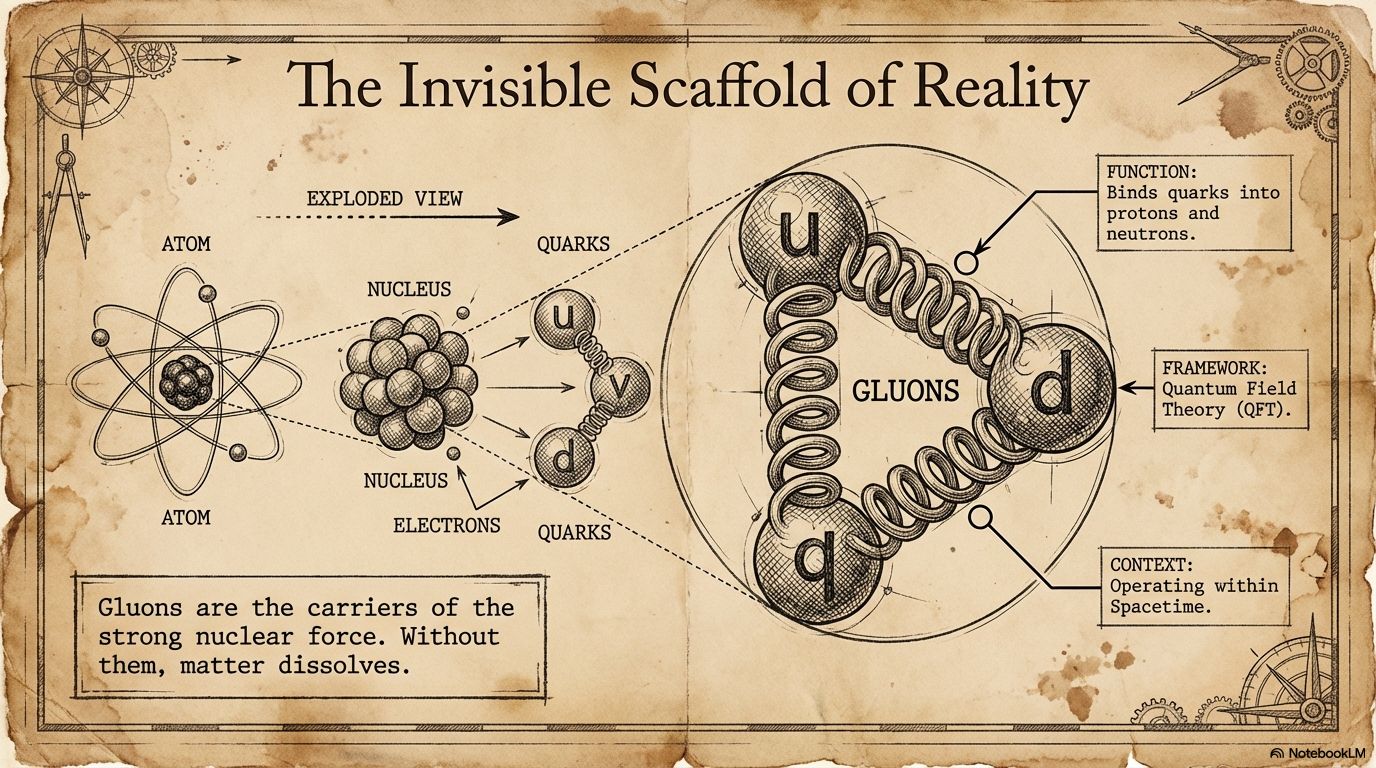
At the heart of this preprint, titled 'Single-minus gluon tree amplitudes are nonzero', available on arXiv, are gluons — particles so fundamental that without them, matter itself wouldn't exist.
An internal scaffolded version of GPT-5.2 spent approximately 12 hours reasoning through the problem to generate the formula and a formal proof of its validity.
ALSO READ: Anthropic Drops Claude Risk Report Days After Its AI Safety Chief Resigns
Invisible Glue Holding Everything Together
Gluons are essentially the smallest building blocks of reality known. They carry the strong nuclear force that binds fundamental subatomic particles (quarks) together, to form protons and neutrons. Without gluons, quarks would drift apart, atomic nuclei would collapse, and the physical world, as we know it, would fall apart.
Physicists study gluons to understand atoms, but also to understand the mathematical framework around reality and the forces governing it. These particles are described and understood by quantum field theory, which combines quantum mechanics and Einstein's theory of special relativity.
For context, the concept of special relativity pertains to space, time, and energy at constant motion. It says that space and time aren't fixed but are linked in "spacetime," which can stretch and warp; the faster you move or the stronger the gravity, the slower time passes for you compared to others, and the speed of light is the universe's ultimate speed limit.
Predicting The Impossible
At the subatomic scale, physics is governed by probability. Instead of predicting exact outcomes, physicists calculate the likelihood that particles will interact in certain ways. These probabilities are then encoded in mathematical objects called 'scattering amplitudes.' It describes the probability amplitude (the maximum displacement or distance moved by a point on a vibrating body from its equilibrium) of a particle scattering in a particular direction relative to an incoming wave.
An analogy to explain this would be traffic at a junction. You cannot predict exactly when two cars will collide, but you can predict the probability based on their speeds and directions. Similarly, in particle physics, scattering amplitudes play a similar role, predicting how particles collide and interact.
When the amplitude equals zero, it means the interaction cannot occur. For years, physicists believed that when one gluon spins in one direction, and the others spin in the opposite direction, the interaction's probability was exactly zero.
New Research
The new research shows that the zero-probability conclusion depended on an assumption that the particles involved were moving in generic, ordinary trajectories.
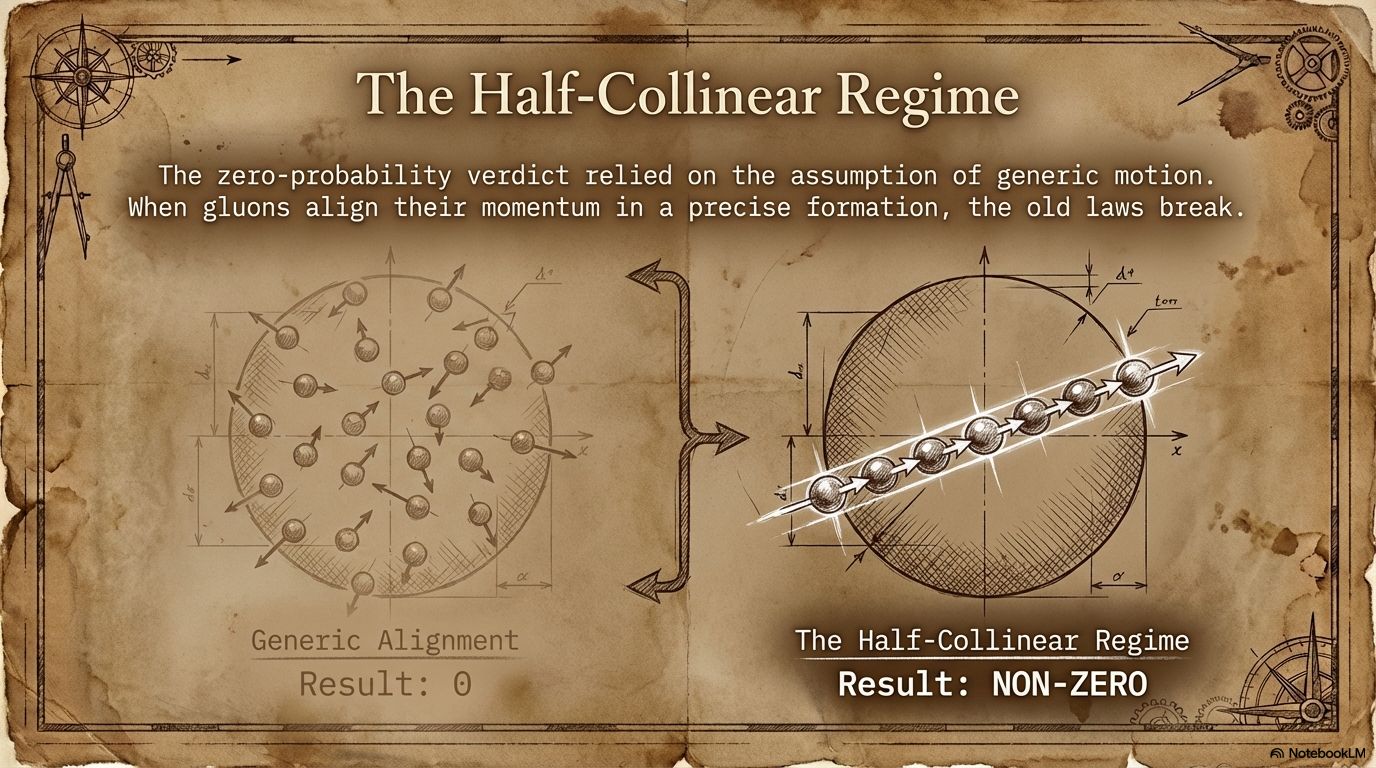
But under a special and highly precise alignment, known as the half-collinear regime, that assumption breaks down. In this, the gluons' momentum lineup in a particular way that changes a long-standing theory. This subtle distinction now allowed physicists to calculate the amplitude and show that it is not zero after all.
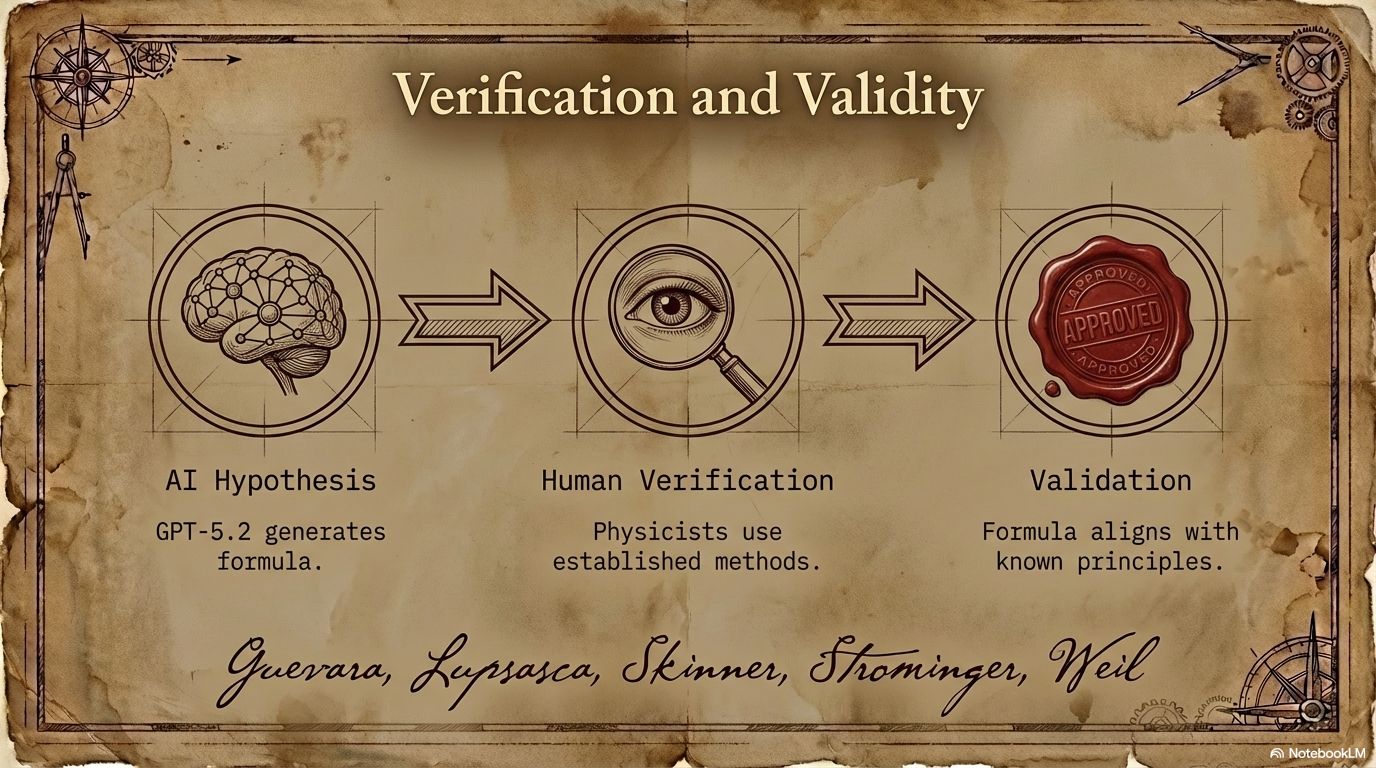
The preprint's authors — Alfredo Guevara, Alex Lupsasca, David Skinner, Andrew Strominger, and Kevin Weil — initially worked out the interaction formulas for different numbers of gluons, calculating cases up to six particles manually. These efforts resulted in highly complex expressions that proved difficult to generalise or simplify.
Where AI Made the Difference
At that point, GPT‑5.2 was brought into the process. An internal version of the model then worked through the mathematical reasoning and produced a formal proof. The human researchers verified the result using established physics methods, confirming that the formula was correct and consistent with known principles.
In theoretical physics, simple formulas often signal deeper truths. Many of the most important discoveries in physics — from Einstein's theory of relativity to the equations governing electromagnetism — emerged from finding simple mathematical relationships hidden beneath complex calculations.
This new formula suggests there are previously unexplored structures within quantum field theory. It provides physicists with a new tool for understanding gluons and the strong force, and it may help uncover further hidden relationships between particles.
Why Finding a Simple Formula Matters
The researchers have already extended their methods to study gravitons, the hypothetical particles believed to carry gravity. While gravitons have not yet been observed, studying their mathematical properties could help physicists move closer to unifying quantum mechanics and gravity—one of the biggest unsolved problems in science.
As theories grow more sophisticated, the calculations required to explore them become increasingly difficult. AI systems like GPT-5.2 offer a way to navigate this complexity, helping scientists identify patterns and generate hypotheses more quickly.
"I am already thinking about this preprint's implications for aspects of my group's research program. This is clearly journal-level research advancing the frontiers of theoretical physics, and its novelty will inspire future developments and subsequent publications," said Nathaniel Craig, professor of physics at the University of California.
ALSO READ: Is AI Stopping You From Meeting Your Soulmate?
Essential Business Intelligence, Continuous LIVE TV, Sharp Market Insights, Practical Personal Finance Advice and Latest Stories — On NDTV Profit.























