Rupee Outlook Bearish As Risk Reversal, Derivatives Signal Volatility Ahead: RBI Report
The rupee's weakness reflected falling terms of trade due to the impact of tariffs and slowdown in capital flows, the RBI said.

Market indicators have signalled bearish near-term outlook for the Indian rupee, weighed by the impact of US tariffs and slowdown in foreign capital flows, the Reserve Bank of India said in a report on Wednesday.
The INR depreciated by 5% in calendar year 2025 against the US dollar (USD), the sharpest annual decline since 2022, and making it Asia's worst-performing currency. The rupee settled 9 paise weaker at 89.88 on Dec. 31, as per Bloomberg data. The unit hit an all-time low of 91.03 earlier this month.
The rupee's weakness reflected falling terms of trade due to the impact of tariffs and slowdown in capital flows, the RBI said in its Financial Stability Report, December 2025.
Foreign portfolio investors have pulled out Rs 1.66 lakh crore or $19 billion from Indian equities in 2025, while debt inflows was positive at Rs 58,000 crore or $6.6 billion, as per data from the National Securities Depository Ltd.
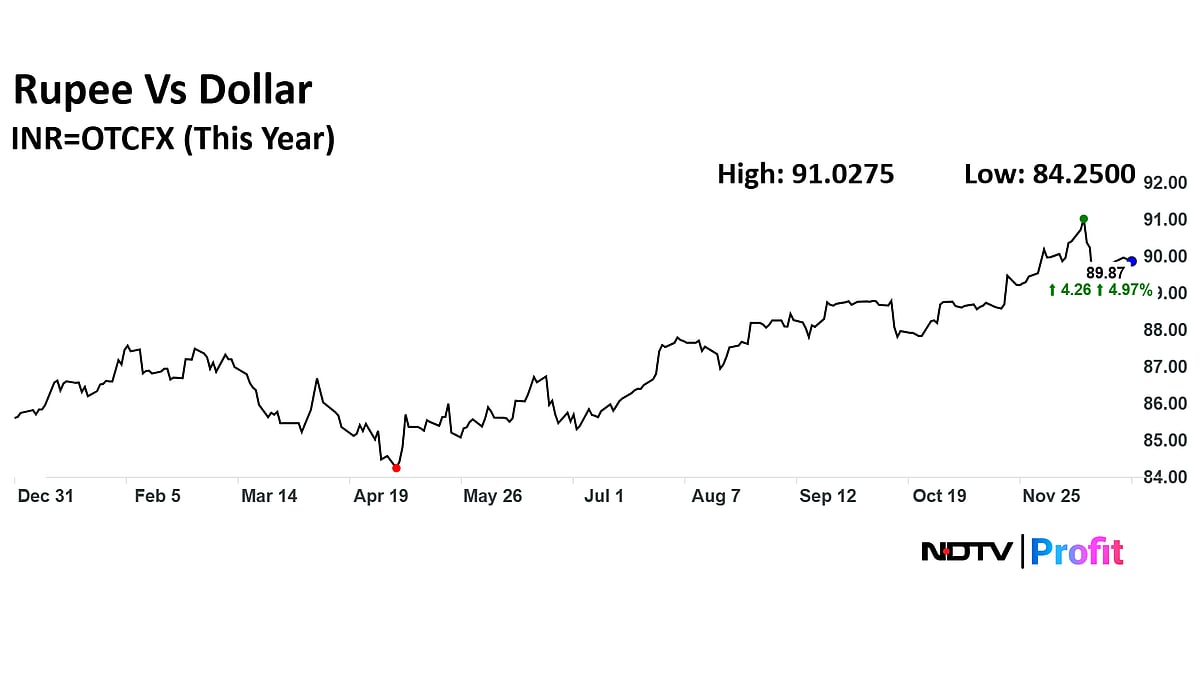
With the effective US tariff rate of 50% on India being the highest compared to its trading partners, the INR depreciated despite the broad weakening of the USD against other major and Asian currencies, according to the RBI.
"The exchange market pressure index indicates the rising depreciation pressure on the INR. Importantly, the exchange rate has displayed wider trading range, which in turn has imparted higher volatility," report said.
"Currency derivatives markets also point to the likelihood of increased volatility going forward as trade tensions continue to weigh on market sentiments. Risk reversal has moved to positive territory, signalling bearish near-term outlook on the Indian Rupee," the RBI said.
Risk reversal compares the cost of call options to put options on a currency. If the value is positive, it means call options are more expensive than puts. This suggests traders expect the currency (in this case, the INR) to fall, indicating a bearish outlook.
The RBI report further noted that the Indian economy is likely to maintain strong growth, underpinned by robust domestic demand, benign inflation, and prudent macroeconomic policies despite an uncertain and challenging global economic backdrop.

