
Japan's industrial production grew at the fastest clip in nearly a year, as manufacturers sought to meet strong demand before the US implements new tariffs on autos and auto parts.
Factory output increased in February by 2.5% from January, the first advance in four months and marking the fastest gain since March last year, the Industry Ministry reported Monday. Economists had expected a 2.0% gain. Output rose 0.3% from a year ago, missing the consensus call of a 1.2% rise.
The ministry also reported that retail sales increased 0.5% in February from January, slightly better than the forecast, while they gained 1.4% versus the previous year.
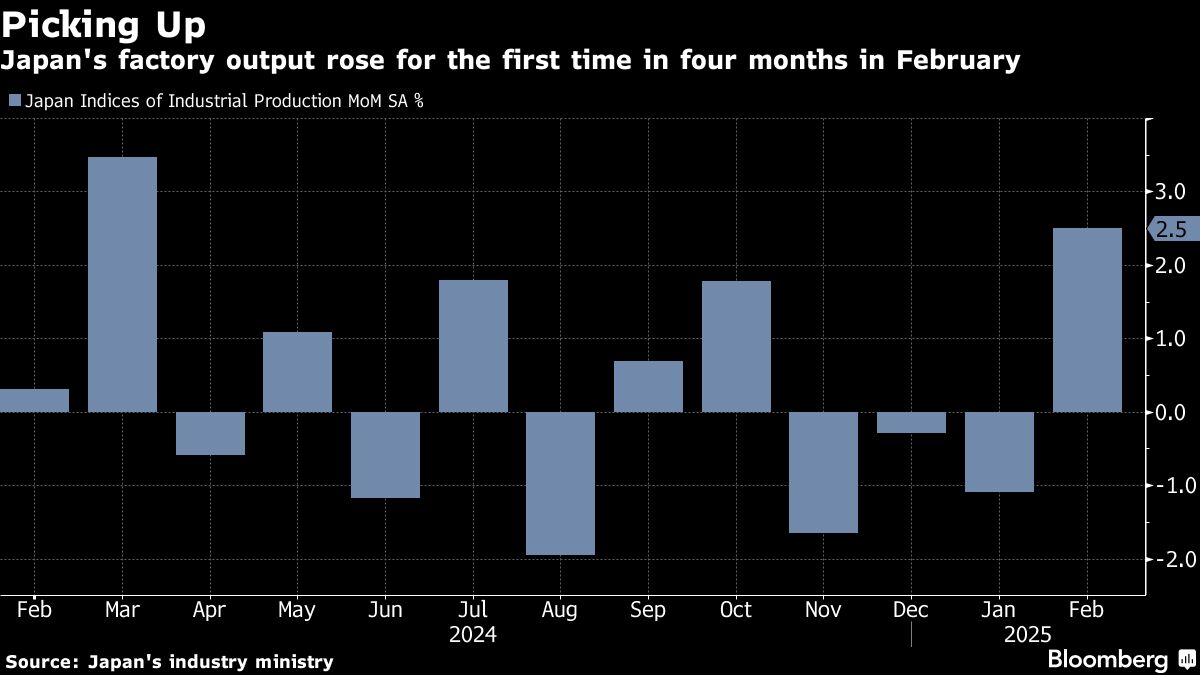
Monday's data are consistent with the Bank of Japan's assessment that the economy has recovered moderately even though there are pockets of weakness. Authorities will monitor closely to see if the rebound in output can be sustained in the face of rising tariffs in the US. US President Donald Trump signed an order last week to impose a 25% tariff on foreign-made vehicles effective April 3, with some auto parts to be added in May.
“Production remains in a phase of rebound from a decline,” said Yutaro Suzuki, an economist at Daiwa Securities. “With the slowdown in overseas economies, including the US, intensifying, Japanese production will likely remain sluggish or grow very slowly.”
The new duties in the US are in addition to steel and aluminum tariffs introduced earlier this month and so-called reciprocal duties set to be announced early next month. For now, output is forecast to rise 0.6% and 0.1% month on month in March and April, respectively.
“Since Trump's comments on trade policies have been changing daily, businesses are finding it difficult to make decisions about the future,” Suzuki said. “Companies are becoming more cautious about capital investment.”
Among sectors reporting increases in output in February were electronic parts and devices and paper and pulp, with autos barely positive at plus 0.2%. Industries reporting declines included transportation machinery excluding autos, oil and coal products and steel and non-ferrous metals.
What Bloomberg Economics Says... “Japan's February industrial production report shows semiconductor-related demand drove a brisk rebound in output. A survey of manufacturers in the same report suggests they will continue to ramp up production of such goods in March. Together, this bodes well for first-quarter GDP growth.”— Taro Kimura, economistClick here to read the full report
The figures highlight the mixed dynamics at work in Japan's economy. The latest round of annual wage negotiations resulted in pledges by employers to offer the biggest wage increases in more than three decades, underscoring the competition to lure and retain staff in a tight labor market.
It was the second year of wage gains exceeding 5% for companies under the umbrella of Rengo, the Japanese Trade Union Confederation. Even so, the impact on spending has been muted due to sticky inflation. Private consumption was barely positive in the fourth quarter, and household spending has been spotty.
The BOJ's Tankan survey due for release Tuesday is expected to highlight a different kind of disparity by showing that sentiment remains positive at large companies, while the gauge for small manufacturers is forecast to turn negative.
Amid the mixed trends, Japan's auto sector is likely to come under particular pressure. The Trump administration's latest tariffs could reduce the nation's car production by 5.8%, while auto output in Canada and Mexico — which includes production from Japanese-owned factories — is expected to decline by 26.6% and 20.3% respectively, according to a forecast by Kenichi Kawasaki, a professor at the National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies.
The policies risk triggering retaliation steps from affected countries, further heightening global uncertainties and potentially undermining business sentiment.
With the global economy likely to face major disruptions, Japan may need to rely more on domestic demand to sustain growth.
Both domestic economic concerns and recent US policies present a political test for Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba, whose Liberal Democratic Party performed poorly in a national election in October, shortly after he became premier. Ishiba faces his next electoral challenge in an upper house elections this summer.
The Japanese government has urged the US to exempt Japan from the auto tariffs, while pledging comprehensive measures to protect jobs affected by the policy. Separately, the government signaled last week that it plans to introduce measures to mitigate inflation, drawing on existing budget allocations.
Essential Business Intelligence, Continuous LIVE TV, Sharp Market Insights, Practical Personal Finance Advice and Latest Stories — On NDTV Profit.























