
Macro stress tests aim to assess the resilience of the banking system to macroeconomic shocks. The tests project capital ratios of banks under three scenarios — a baseline and two adverse macro scenarios over a two-year horizon, incorporating credit risk, market risk and interest rate risk in the banking book in the framework.
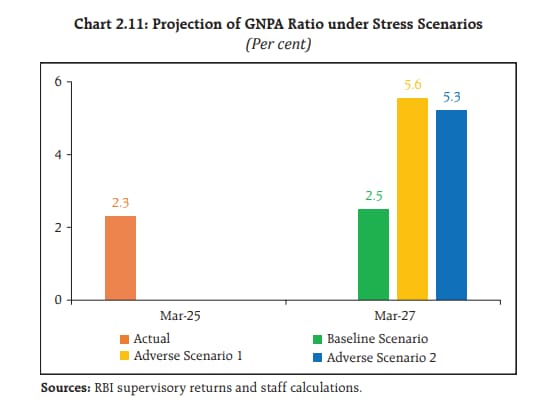
The macro stress tests by India's central bank indicate resilience of scheduled commercial banks to macroeconomic shocks. The aggregate gross-non-performing-asset ratio of the 46 banks may marginally rise from 2.3% in March 2025 to 2.5% in March 2027 under the baseline scenario and to 5.6% and 5.3% under the adverse scenario of geopolitical risk and adverse scenario of global growth slowdown respectively.
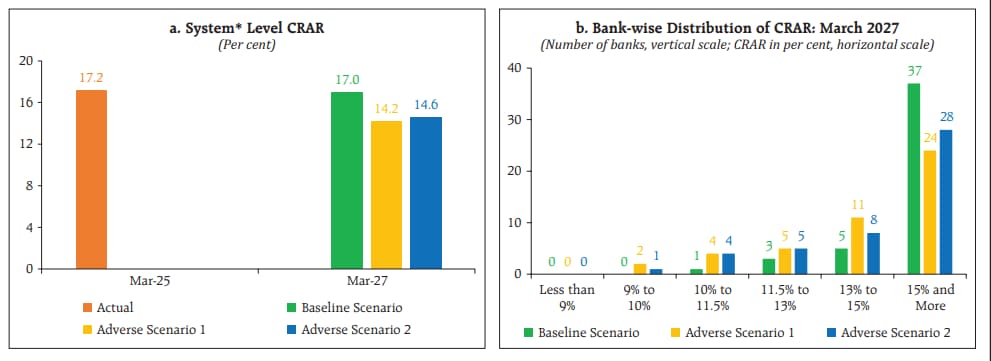
The results revealed that the aggregate capital adequacy ratio of major scheduled commercial banks may marginally dip to 17% by March 2027 from 17.2% in March 2025, under the baseline scenario.
It may decline to 14.2% under the adverse scenario of geopolitical risks and to 14.6% under the adverse scenario of global growth slowdown. However, none of the banks will fall short of the regulatory minimum requirement of 9% even under the adverse scenarios.
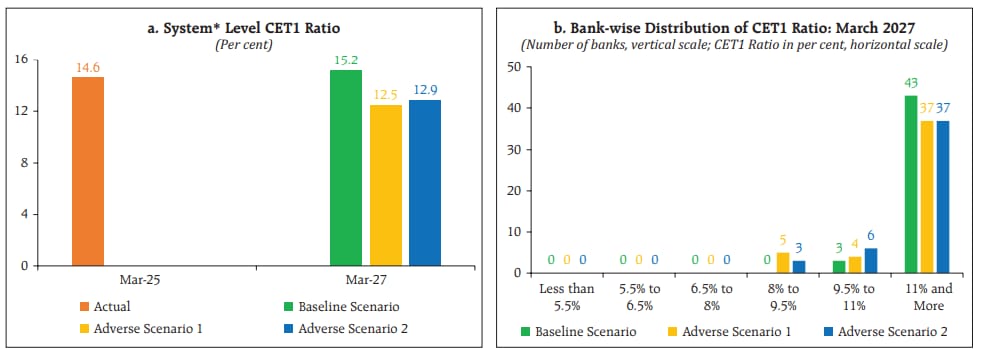
The Common Equity Tier 1 ratio of the banks may rise from 14.6% in March 2025 to 15.2% by March 2027 under the baseline scenario. However, it may fall to 12.5% under the adverse scenario of geopolitical risks and to 12.9% under the adverse scenario of global growth slowdown. None of the banks will breach the regulatory minimum requirement of 5.5% under any of these scenarios.
The soundness and resilience of scheduled commercial banks are bolstered by robust capital buffers, multi-decadal low non-performing loans and strong earnings, the report stated.
The resilience of the non-banking financial companies is bolstered by enhanced asset quality and healthy capital buffers. Interconnectedness among financial sector entities, as reflected in their bilateral exposures, continued to grow in double-digits, it added.
The capital position of the urban cooperative banks strengthened, while that of the NBFCs remained well above the regulatory minimum. The consolidated solvency ratio of the insurance sector, both life and non-life segments, remained above the minimum prescribed threshold limit, according to the report.
Stress-test results of mutual funds and clearing corporations affirm their resilience to shocks, the report said.
Essential Business Intelligence, Continuous LIVE TV, Sharp Market Insights, Practical Personal Finance Advice and Latest Stories — On NDTV Profit.























